What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is an Open Source cloud computing platform that provides a stack of tools and services to build & manage On-Premise Private cloud (IaaS) infrastructures.
It offers virtualization, storage, and networking, Orchestration capabilities, allowing organizations to create and customize their cloud environments.
When was OpenStack Developed?
Openstack’s development started in October 2010, with its first official release, code-named “Austin”.
Current Version: Antelope 2023.1 & beta 2023.2 Bobcat
OpenStack was initially developed by RackSpace & NASA in collaboration.
It become Industry Standard for Private Cloud & Get Contributed for Development from global community of developer & organizations.
Where was OpenStack Deployed?
OpenStack can be deployed in different locations and scenarios depending on the user’s requirements and preferences. Some of the common deployment options are:
On-premises: Company deploy OpenStack on their own servers within their data centers . Option gives more control over their cloud infrastructure & data security but also requires maintenance and management efforts.
Public Cloud: OpenStack on a public cloud service provider’s data centers or servers. Option gives users more convenience and flexibility associated with sharing resources with other tenants.
Edge: Users can deploy OpenStack at the edge of the network or closer to the end-users or devices. Option gives users more performance and latency benefits in terms of connectivity and scalability.
Why was OpenStack Created?
OpenStack was created to create Open Source private cloud on On-Premise with this key motivations:
– Avoiding Vendor Lock-in : To provide an open and vendor-neutral alternative to proprietary cloud solutions.
– Promoting Innovation : By fostering collaboration and competition among technology providers.
– Customization and Control : Enabling organizations to tailor their cloud infrastructure to specific needs.
– Cost Savings : Offering cost-effective cloud solutions compared to proprietary alternatives.
– Compatibility and Integration: Facilitating integration with other technologies and existing IT infrastructure
Who Uses OpenStack?
OpenStack is used across Industry & Sector:
– Telecommunication
Telecom use OpenStack (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) infrastructures, IoT , 5G
– Information Technology
Edge Computing Content Delivery Network (CDN)
– Research & Deplopment Projects and AcademicAcademics
Organizations use OpenStack for scientific computing and data analysis, High Performance Computing(HPC).
– Service Providers
Cloud providers use OpenStack as the undercloud infrastructure for offering Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
– Private Cloud
Organization Build On Premise Private Cloud with undercloud & overcloud deployments
– AI MLOPS Projects
AI Cloud and MLOps deployed and on undercloud to provide overcloud services
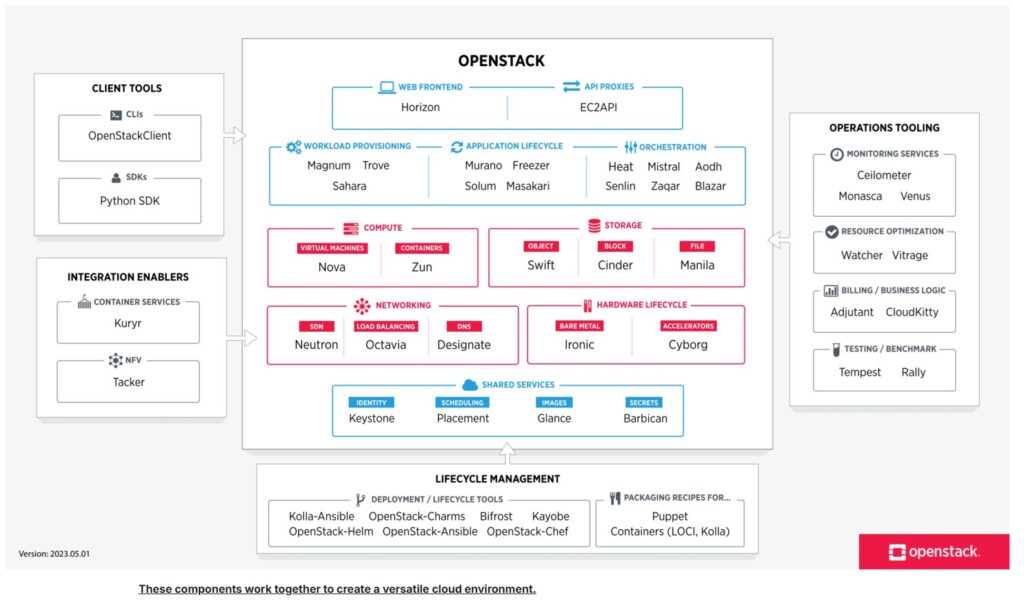
How Does OpenStack Work?
OpenStack is composed of various services that collectively work to manage cloud infrastructure:
Nova: Manages virtual machines, providing computing resources.
Cinder: Offers block storage services for attaching additional storage volumes to instances.
Swift: Provides scalable object storage suitable for handling large amounts of unstructured data.
Neutron: Manages networking services, including creating and configuring networks, routers, and load balancers.
Horizon: Offers a web-based dashboard for users to interact with and manage OpenStack services.
Keystone: Provides identity and authentication services, ensuring secure access control to all components.
Glance: Handles virtual machine image storage and management, allowing easy provisioning of VMs.
Heat: Manages orchestration and automated deployment of cloud applications using templates.
Ceilometer: Telemetry and monitoring services to collect data on resource utilization & system performance.
Trove: Provides Database as a Service (DBaaS), simplifying the management of database instances.
Magnum: Manages container orchestration engines, to deploy and manage containers in OpenStack.
Ironic: Enables bare-metal provisioning, allowing users to manage physical servers as well as virtual machines.
Current Market Size
Global Services market was valued at 4.54$ billion in 2021 & forecast to reaching 17.95$ billion by 2027.
OpenStack Persona Ecosystem
Cloud Administrator
– Responsible for the overall management and administration of the OpenStack cloud.
– Manages compute, storage, and networking resources.
– Configures and monitors the health of the cloud infrastructure.
Tenant/User:
– Utilizes the OpenStack cloud to deploy and manage workloads.
– Creates and manages virtual machines, storage, and networking resources.
– Interacts with the Horizon dashboard or uses OpenStack APIs for resource management.
DevOps Engineer:
– Focuses on the automation and integration of development and operations processes.
– May use OpenStack Heat for orchestrating and automating infrastructure deployments.
Cloud Architect:
– Designs and plans the overall cloud architecture using OpenStack.
– Determines resource requirements, scalability, and integration with other system
Network Administrator:
– Manages and configures networking components within the OpenStack environment.
– Configures routers, subnets, and network security groups.
Operations and Support Teams:
– Monitor the health and performance of the OpenStack environment.
– Provide support and troubleshooting for users and tenants.
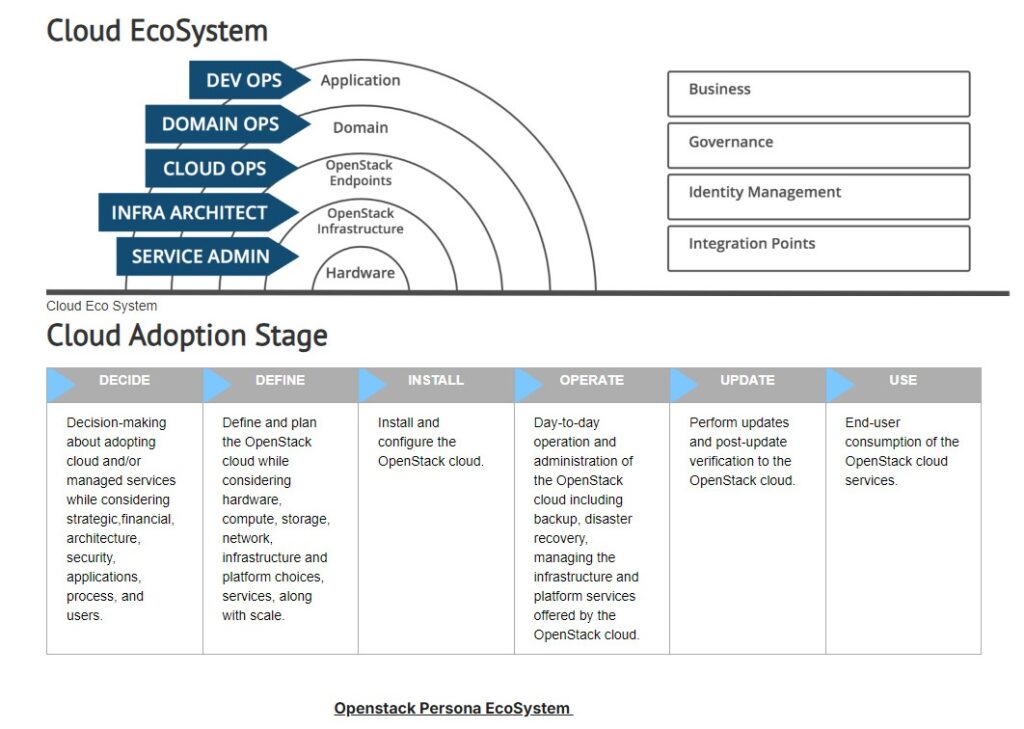
Understanding these personas helps in tailoring the OpenStack experience for different user roles and responsibilities. OpenStack’s flexibility allows it to cater to various use cases and organizational structures, and different personas play crucial roles in the successful deployment and operation of OpenStack-based clouds.
OpenStack Product Developed by Industry Leaders:
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
- Huawei FusionSphere
- Mirantis Open Stack Private Cloud
- Cisco Metacloud
- HPE Helion
- IBM Openstack
- VMware Integrated OpenStack (VIO)
- Canonical OpenStack
- SUSE OpenStack